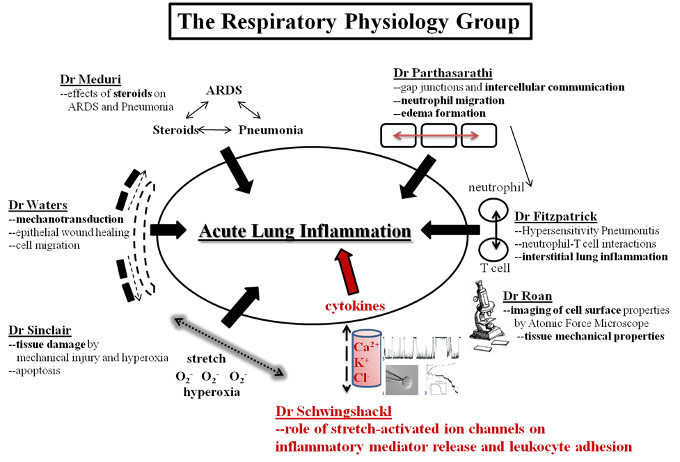
Respiratory Physiology Group
The Department of Physiology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center is consistently ranking among the top 10 Physiology Departments in the country in extramural funding. Although the research projects of the faculty are diverse, several investigators recognized their common research interests and formed the Respiratory Physiology Group with its main focus on lung injury. Within a short period of time investigators outside the Department with similar research interests joined this diverse group transforming it into today’s well-organized and structured multidisciplinary group of investigators with a common focus on lung inflammation and lung injury.
The group is currently composed of senior and junior faculty members of the UT Departments of Physiology, Molecular Sciences, Pulmonary Medicine, Pediatrics, Pharmaceutical Services, a faculty member from the Biomedical Engineering Department of the University of Memphis, several postdoctoral fellows, graduate students, laboratory technicians and summer students.
 Dr. Schwingshackl’s research interest lies in investigating the role of stretch-activated
ion channels (SAC) in the secretion of inflammatory mediators in the lung. Both, mechanical
stretch and hyperoxia appear to induce expression of stretch-activated ion channels
in lung tissue. Inhibition of these channels may constitute a novel target to reduce
inflammation in the lungs of mechanically ventilated children.
Dr. Schwingshackl’s research interest lies in investigating the role of stretch-activated
ion channels (SAC) in the secretion of inflammatory mediators in the lung. Both, mechanical
stretch and hyperoxia appear to induce expression of stretch-activated ion channels
in lung tissue. Inhibition of these channels may constitute a novel target to reduce
inflammation in the lungs of mechanically ventilated children.
Respiratory Physiology Lab: Selected Publications
- Schwingshackl A, Teng B, West AN, Makena P, Gorantla V, Sinclair SE, Waters CM. Regulation and function of the two-pore-domain potassium channel Trek-1 in alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2012, 302:L93-102.
- Ghosh MC, Makena PS, Gorantla VK, Sinclair SE, Waters CM. CXCR4 Regulates Migration of Lung Alveolar Epithelial Cells through Activation of
Rac1 and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2).
 Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2012 (in press).
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2012 (in press). - Makena PS, Gorantla VK, Ghosh MC, Bezawada L, Kandasamy K, Balazs L, Luellen CL, Thompson
KE, Parthasarathi K, Ichijo H,Waters CM, Sinclair SE. Deletion of Apoptosis Signal Regulating Kinase-1 Prevents Ventilator-induced Lung
Injury In Mice.
 Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 (in press).
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 (in press). - Makena PS, Gorantla VK, Ghosh MC, Bezawada L, Balazs L, Luellen C, Parthasarathi K,
Waters CM, Sinclair SE. Lung injury caused by high tidal volume mechanical ventilation and hyperoxia is dependent
on oxidant-mediated c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation.
 J Appl Physiol, 2011, 111:1467-7.
J Appl Physiol, 2011, 111:1467-7.
