Smart Goals
Goals are impacted by...
- The students in your course
- All have differing backgrounds, learning experiences, interests and aptitudes
- All have differing expectations for the instructor and the course
- The course design framework selected
- The learning environment(s) in which the learning will occur
- The course expectations inside and outside of class meetings
- The teaching strategies and approaches utilized
- The possible assessment tools and formats that will be employed
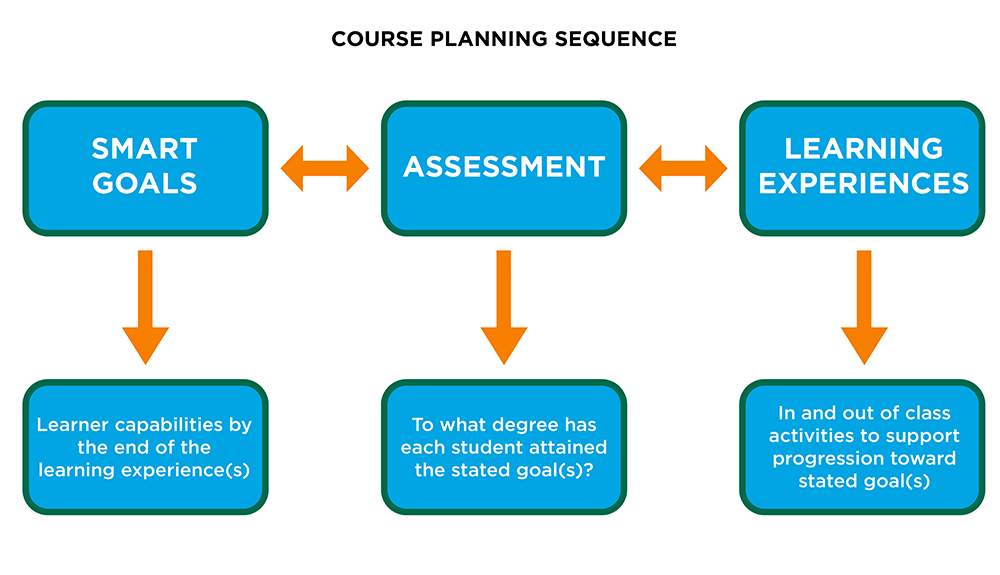
SMART Goals
- Are the first step in designing a course (see diagram above)
- Requires clearly articulating what the learners will be able to do (behavioral) by the completion of the course or learning experiences
- Well-articulated goals increase learner motivation (Locke and Latham, 2002)
- They direct effort and attention
- High/moderately difficult goals elicit greater effort
- Increase persistence
- Greater use of task-relevant knowledge
- SPECIFIC (see Bloom's Taxonomy – Revised and Digitalized)
- MEASURABLE (behavioral and observable)
- ATTAINABLE and realistic for the capabilities of the learners and within the allotted time span
- RELEVANT and meaningful to the learners, course experiences and ultimate application of the learning
- TIME-BOUND (e.g. by the end of the course)
Examples
Potential SMART Goals in the health sciences:
- Dentistry
- By the completion of the course, the students will be able to sequence the steps/procedures for administering intravenous sedation and general anesthesia to an adult patient for oral surgeries
- By the completion of the course, the students will be able to administer in the appropriate sequence intravenous sedation and general anesthesia to an adult patient for oral surgeries
- Medicine
- By the completion of the clinical, the students will be able to differentiate between written symptoms of diabetes and anemia for 5 patients of varying demographics
- By the completion of the clinical, the students will be able to differentiate between and accurately diagnose 5 patients with similar symptoms
- Pharmacy
- By the completion of the clinical, the students will be able to accurately assess research resources and associated literature to identify specific evidence-based drug information to meet the needs of at least 3 patients of different demographics
- By the completion of the clinical, the students will be able to clearly and accurately explain specific evidence-based drug information to at least 3 different patients of varying demographics
Creating Pertinent Goals/Objectives
- Threshold Concepts
- Bloom's Taxonomy – Revised and Digitalized
- Multiple Intelligence Theory
- Assessment and Outcomes – Western Washington University
References
Locke, E. A., and Latham, G. P. (2002). Building a practically useful theory of goal setting & task motivation: A 35year odyssey. American Psychologist, 57, 705–717
